who is a parasite

- plague
- typhus
- tuberculosis
- tetanus
- Meningitis etc.
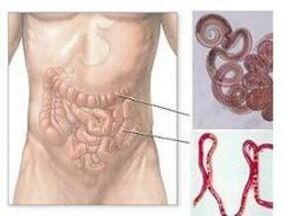
Parasites are organisms that exist entirely at the expense of their host. Unlike other organisms that live in symbiosis with the human body, their life activities can cause continuous harm to the human body. Parasites include: protozoa, bacteria, fungi, and worms.
Parasitic infection route
- Nutritious– through contaminated food, water;
- contact family– Infection occurs through contact with contaminated objects, household members, pets;
- communicable– Infection through blood-feeding insects;
- positive– Parasites enter the body when interacting with contaminated soil or swimming in ponds.
Nutrition

Dried, smoked or dried fish poses a serious hazard. For example, raw pike caviar may be infected with a wide range of tapeworms. Diphyllobothriasis is a disease caused by this worm. The large tapeworm can grow up to ten meters long and live in the small intestine for decades.
Contact details and family
Route of infection
active infection pathways
How to identify internal parasites

- constipate. Due to their size and large numbers, certain types of worms can cause blockages in various body systems: bile ducts, intestines. These blockages can lead to some type of disease and, in particularly severe cases, require surgical intervention.
- diarrhea. Parasites produce substances similar to prostaglandins due to their life activities, causing frequent and loose stools in the host.
- abdominal bloating. During their life, worms often cause intestinal inflammation. These inflammatory processes can lead to the formation of excess gas, which can lead to bloating.
- allergy. Damage to the lining of the gastrointestinal tract can allow undigested food molecules to enter the bloodstream. In this case, the immune system comes into play, and as a result of its reaction, large numbers of eosinophils (cells that cause inflammation) are released into the blood, indicating an allergic reaction in the body.
- bad skin. Many different skin conditions can be caused by microorganisms that live on the skin.
- weight problem. Deviations in weight from normal, either an increase or a decrease, can be a sign of the presence of parasites in the body. Weight loss occurs due to indigestion and loss of appetite. Some worms lower blood sugar levels, causing uncontrollable hunger in the host, leading to obesity.
- chronic fatigue. Weakness, flu-like symptoms, apathy, difficulty concentrating, and poor memory are common symptoms of malnutrition. If you are infected with worms, the function of your digestive system will be impaired, which will affect the absorption of various nutrients, leading to chronic fatigue.
- airway inflammation. Some types of worms move throughout the body, including the respiratory system. In some cases, they can cause lung damage, leading to coughing and fever. Roundworms can even cause illnesses such as pneumonia.
- nervous. The human nervous system can be severely damaged by exposure to worm waste. Various neurological disorders are signs of worm poisoning in the body.